Physics Of The Laser
LASER – Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
Devices of this type are optical amplifiers that emit light energy, which moves in the form of waves, like ordinary light.
The laser was first mentioned in 1917 in A. Einstein’s publication “The Quantum Theory of Radiation”. He theoretically justified the processes that should occur when the energy is emitted by the laser.
Then, in 1954, the Soviet scientist Nikolai Gennadyevich Basov and Alexander Mikhailovich Prokhorov designed the Ammonia MASER (Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)
Similar work was carried out in the United States by the physicists
Charles Hard Townes и Arthur Leonard Schawlow


In 1964, Prokhorov, Basov, and Townes were awarded the Nobel prize in physics for their contributions to science. Schawlow was awarded the Nobel prize in 1981 for his further study of laser properties.
I would like to say a little about the difference in lasers, as many people were looking for and faced with a variety of lasers. They say everything is fine: the specifications are good, the wavelengths are the same, etc. But why then such different prices from $ 1000 to ….. unlimited.
Let’s see what is the cost of the laser.
The main components responsible for the efficiency of the laser system are:
- Nd: YAG crystal

- Pump lamp

The remaining components of the laser system ensure the normal operation of these two components. These elements are located in the handle of the laser, which shoots.
These elements are not visible and there are no descriptions for them. So, you take a pig in the poke, as when choosing, you look at the wavelengths, but the wavelengths are the same everywhere since this is a neodymium laser.
In terms of power, I would advise not to believe the description either. I had the experience of communicating with Chinese manufacturers and when I ordered a device, they asked: “How much power do you need to write on the screen?” We can write a power of 1000 mJ or 2000 mJ. I’m trying to say that what is written on your screen, or instructions to the laser, may not always be true. Therefore, I would recommend do not take this too seriously, when choosing a laser.
Let’s talk about the crystal.
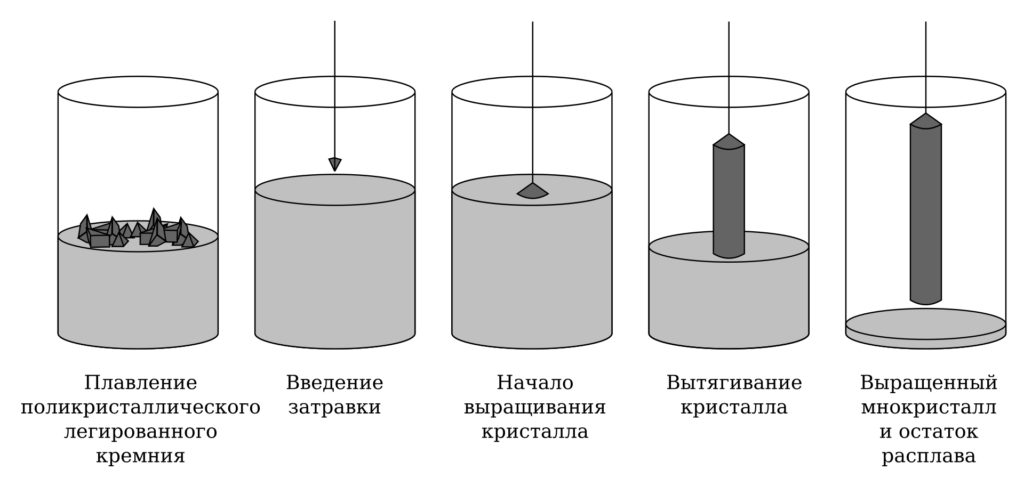
Nd: YAG crystals have more than 30 physicochemical characteristics. These crystals are produced in chemical plants and grown by the Czochralski method.

Jan Czochralski
The Czochralski process is a method of crystal growth used to obtain single crystals of semiconductors (e.g. silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide), metals (e.g. palladium, platinum, silver, gold), salts and synthetic gemstones. The process is named after Polish scientist Jan Czochralski, who invented the method in 1915 while investigating the crystallization rates of metals. He made this discovery by accident while studying the crystallization rate of metals: instead of dipping his pen into his inkwell, he dipped it in the molten tin and drew a tin filament, which later proved to be a single crystal.
The most important application may be the growth of large cylindrical ingots, or boules, of single crystal silicon used in the electronics industry to make semiconductor devices like integrated circuits. Other semiconductors, such as gallium arsenide, can also be grown by this method, although lower defect densities, in this case, can be obtained using variants of the Bridgman-Stockbarger technique.
Nd: YAG crystals are distinguished by the following characteristics:
Nd atom concentration
Crystal lattice structure
Polarization
Optical transmission
Refraction coefficient
Nd partition coefficient
Crystal ends polishing
Cut angle.
etc.
If you search Nd: YAG crystal on Amazon, eBay or any other global marketplace, you will see a variety of options ranging from $ 100 to $ 4000 per crystal only. Here is a price spread due to the quality of the crystal. A good quality crystal should cost at least 1500-1700 dollars – only crystal! The larger its diameter and length, the better will be the flash.
The more expensive and better the crystal, the more productive will be our work with you. This affects efficiency – how quickly you will destroy the pigment.
There are cases when the client goes to the laser removal procedure 5-6 times, but there is no effect. Then he goes to another salon, where more expensive equipment for removal and after 1-2 sessions nothing is left. Here the principle works: the more expensive the better.
How to choose a laser?
Nowadays there are many offers from the Chinese market, and most of the artists use these lasers.
Imagine such a picture. We take the laser to remove which costs $ 1500. The seller who sells laser equipment should have its profit, it usually amounts 30-40% + delivery to the country, as a result, the base cost of the laser equipment falls to $ 700-800. Second, the Chinese are also not altruistic and sell at a profit, and the cost price drops even lower to about $ 500. At the same time, these 500 dollars should include such components as:
- Crystal
- Lamp
- Housing
- Electronics
- Display
- Packing
Under such conditions, there is a saving on everything and on the crystal as well. Therefore, I recommend using your maximum budget to buy a laser. Because here you will not be able to buy now a cheaper device, work and then buy the more expensive one. The quality and efficiency of the process will suffer. As a result, you will not cause the trust of your customers.
When you remove quickly and in the minimum number of sessions, it will be good for your credibility and customers will recommend you to friends, acquaintances, etc.
Ok, let’s move on to the pump lamp.

Lamps as well as crystals are different and differ in such characteristics as:
The volume of the gas discharge chamber
The gas pressure in the chamber
Thorium alloying of tungsten contact elements
The quality of quartz glass.
The difference may lie in the fact that in some lamps the resource of flashes is 400-500 thousand, and in others up to 2-2.5 million and more.
In low-cost lasers, there might be a lamp, which is 400-500 thousand will become unusable and will require replacement.
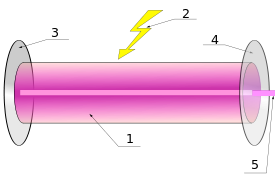
- Crystal
- Energy from pumping lamp
- Total reflector
- Partial reflector
- Laser Light
The device of all lasers is about the same. What happens when you press the laser start button:
First of all, when adjusting the power on the screen, we adjust the pump lamp. That is the flash power that it will give. The first thing that will react to pressing the start button of the laser is the pump lamp. The crystal is a passive thing and in itself, it generates nothing. Therefore, before the crystal generates a beam, it must be pumped with energy, so this lamp is called a pump lamp. Xenon lamp gives a very powerful bright flash, the laser absorbs about 10% of the flash and everything else goes into the heating. In this regard, the cooling system of the laser installation should be good enough that the laser does not overheat.
Further
There was a flash from the lamp which caused the excitation of atoms in the neodymium crystal.
Neodymium atom model
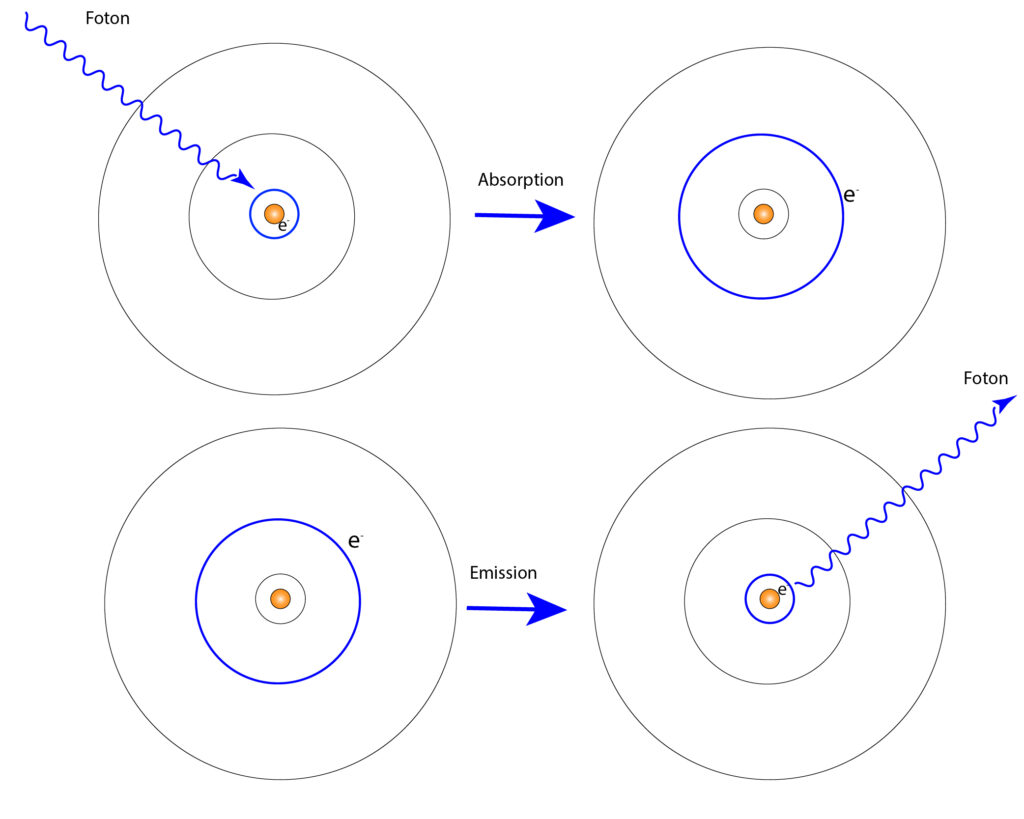
The neodymium atom absorbs the flash from the lamp, while its state is excited. From the first orbit, the electron passed to the second. Since this excited state is not stable, the neodymium atom tries to get rid of this excess energy and the emission occurs, and the atom has released excess energy. It absorbed one energy and released energy with slightly different properties. These properties of the laser beam are quite specific:
- Monochromaticity is when the wavelength depends on the type of atom or molecule being excited. The light consists of a single color or a narrow range of colors. A wavelength of 1064 nm is the wavelength that neodymium atoms emit. There are Alexandrite lasers, which emit a wavelength of 755 nm, there are Ruby lasers with a wavelength of 694 nm. The wavelength depends on the material contained in the crystal. So, certain atoms emit different wavelengths.
- Coherence means that all light quantum go in one phase
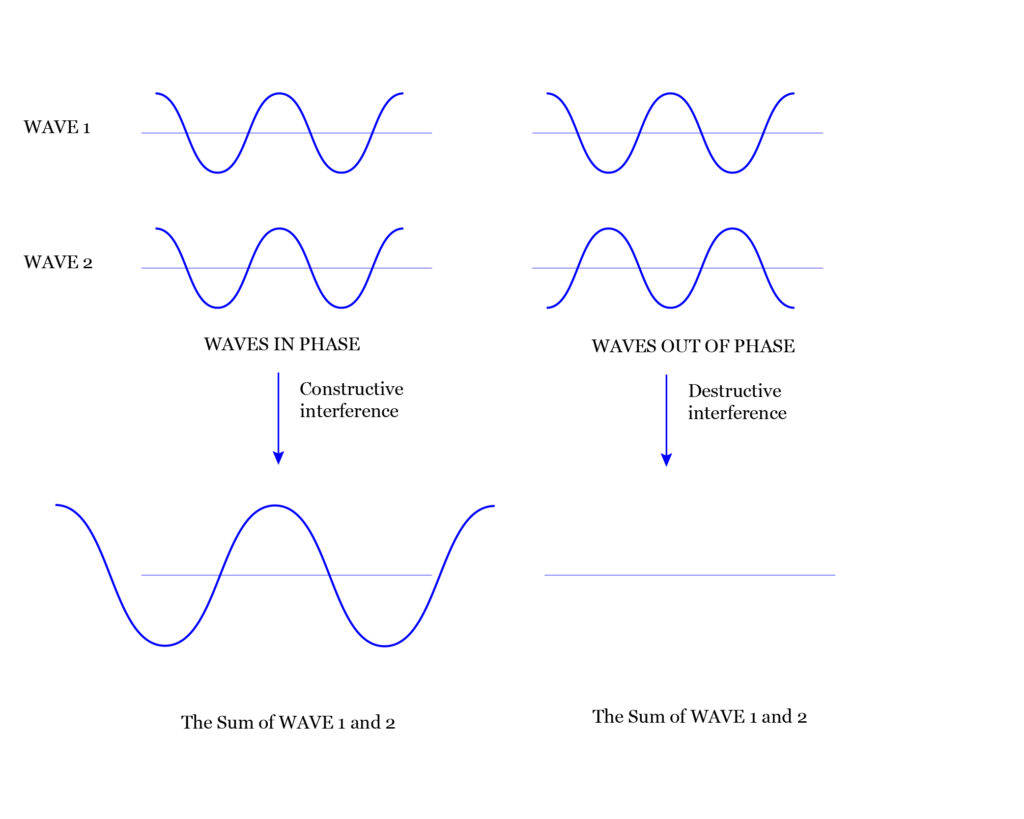
It would seem that the crystal absorbed only 10% of the energy, but the output will be quite a powerful beam of light, as all the waves move in the same phase and their amplitude forces are summed.
The third property is Collimation.
Collimation is a consequence of coherence – the waves in the light beam maintain parallelism and propagate in one direction over a long distance and the beam carries energy without loss, without losing intensity and without scattering. This allows the beam to be focused into a spot commensurate with the wavelength of the laser radiation. That, in turn, allows you to focus the beam on a very small object and as a result to obtain a biological effect at low energies of laser radiation. Lenses or lens systems in scanners are used to focus the beam.

I am telling you this not for passing the exam or something else. I just want you to understand the laser device itself and how it works so that the laser handpiece wouldn’t seem to you an incomprehensible crap with a twisting tip)
Since if you understand how it works, you will be able to analyze and face any unusual situation to find a way to solve it, whether to take up the work and whether you can help the client.
Now let’s try to combine what we have already studied – the skin and the physics of the laser. We will try to understand how the laser works and affects the skin and how it destroys the pigment. Now we’re moving on to the next lesson.
